PAE is a medical procedure that began in 2012 and has since gained popularity. It is a minimally invasive medical procedure used to treat enlarged non-cancerous prostate glands. PAE uses advanced technology to treat benign prostate hyperplasia, also called BPH, a prevalent condition in aging men.
Prostate Artery Embolization reduces urinary tract symptoms caused by BPH, such as bladder and kidney problems. An Interventional Radiologist (IR) uses advanced imaging techniques to view internal body parts and issue treatment without surgery.
The Prevalence of Prostate Artery Embolization
The symptoms of PAE linked to benign prostatic hyperplasia are evident in one in four men 55 years. In the United States, almost half of men 50 years of age have a larger prostate, and 70% of men between 60-69 years and 80% aged 70+ also suffer from benign prostatic hyperplasia.
In case you are among men with such conditions, MG Health has the answers to your problems. MG has some of the best experts in PAE.
The Achievement Rate of Prostate Artery Embolization
[https://pixabay.com/illustrations/kidney-anatomy-biology-body-cancer-3667909/]
PAE boasts high success rates, with more than 90% of males getting relief in a year. On the good side, PAE has no adverse sexual performance side effects, unlike other treatments.
Some studies also indicate that PAE has lifelong success in medicating growing prostate.
A review shows that more than 80% of men are doing well three years into a PAE procedure.
Signs and symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Difficulties in starting urinating or unable to empty your bladder
- Presence of blood in urine, your urine may be pinkish
- Weak urine streams, i.e., stop and start urinating suddenly
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Feeling the urgency to urinate all the time
- Hematuria, bleeding from the enlarged prostate
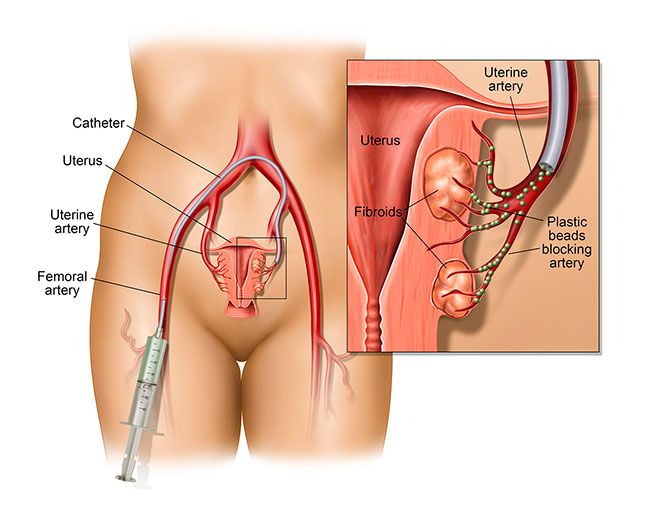
The Process of Prostate Artery Embolization
An IR typically cuts a small hole (incision) on your wrist or upper thigh to access your arteries. Perform PAE. Doctors insert a Foley catheter into an artery inside the urethra and push it towards the prostate to provide a reference point. The radiologist then directs the catheter blood supplying vessels in your prostate.
Once the catheter is in position, the IR injects tiny round particles into the arterial branches through the catheter to reduce or block blood flow. The blockage of these branches is embolization. The radiologist moves the catheter to the other prostate and repeats the procedure.
Embolization deprives the prostate of oxygenated blood, making it shrink and relieve. Hence, improving urinary symptoms after a few days. Once the doctor completes the procedure, they eject the catheter gently from the prostatic arteries.
Embolization lasts about one to four hours, depending on the size and location of arteries in the prostate. Most males feel no pain during the procedure, only a pinch on the wrist or groin at the puncture point.
To reduce anxiety during the process, a doctor may prescribe mild sedatives like Fentanyl. Otherwise, patients usually stay awake during the entire procedure.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
As mentioned earlier, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia is a large prostate gland in older men. BPH can cause urinary problems, but it is not cancer and is not a risk for prostate cancer. If you have the condition, worry less as you have options like PAE to explore.
What are the Advantages of PAE?
PAE is a safe medical procedure for men with BPH. Like many other minimally invasive, PAE has many benefits over traditional surgery.
A year after the procedure, the prostate shrunk by about 30%. As a result, the patient experiences minor urinary symptoms, sparing erectile function, and improves the general quality of life.
Extra benefits of PAE include;
- Quick recovery time; one week
- Minimally invasive procedure
- The procedure is simple and can happen as an outpatient procedure
- Low to nil risk of getting erectile dysfunction or retrograde ejaculation
- For most patients, there is less need to use a catheter
- Less swelling and pain
- There is no risk of unrestraint leakage surrounding healthy tissue
- The complication rate is less than 1%
- A doctor can perform the procedure on a moderate or large prostate gland with no upper size limit
- Prostate-specific Antigen levels drop after the procedure
- PAE reduces lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), e.g., the urgency and frequency of urinating, especially at night. Others are weak urine, straining to urinate, incomplete bladder emptying, and intermittency.
What Are the Risks Of PAE?
Only skilled, qualified and well-trained inter-ventional radiologists should perform PAE. Patients may experience “post-PAE syndrome” for a few days after the procedure. Patients may feel nauseous, vomit, have a fever, abdominal pain, or frequent urination.
Other risks include hematoma at the incision are; blood in urine, semen, or stool. You may also have bladder spasms or an infection of the incision area or prostate.
Please Schedule an Appointment with Us Today
Are you tired of dealing with the side effects of an enlarging prostate? PAE might be the best remedy for your condition. Contact MG Health today and let us answer all questions on prostate health. We have the best medics to diagnose and treat your disorder and walk you through the healing journey.